
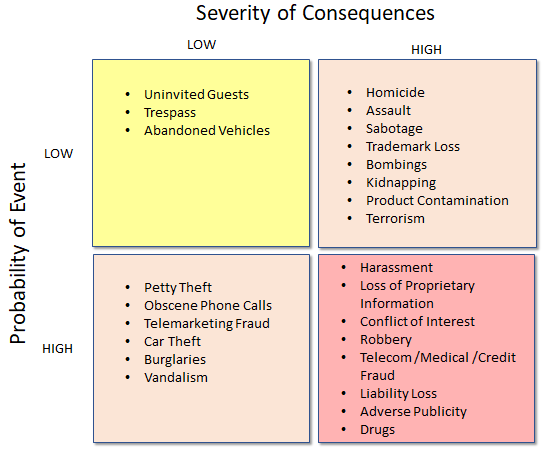
Table 6.2 shows a typical risk impact scale for cost, time, and quality objectives based on a high-high to low-low scale. Cardinal scales are expressed as values from 0.0 to 1.0 and can be stated in equal (linear) or unequal (nonlinear) increments. Cardinal scale values are actual numeric values assigned to the risk impact. The risk impact scale can be a relative scale (also known as an ordinal scale) that assigns values such as high-medium-low (or some combination of these) or a numeric scale known as a cardinal scale. Impact is the amount of pain (or the amount of gain) the risk event poses to the project.

Carefully weigh their responses to come up with the best probability values possible. It's best to fully develop the criteria for determining probability and get as many experts involved as you can. Granted, you're basing your guess on past experiences with similar projects or risk events, but no two risk events (or projects) are ever the same.
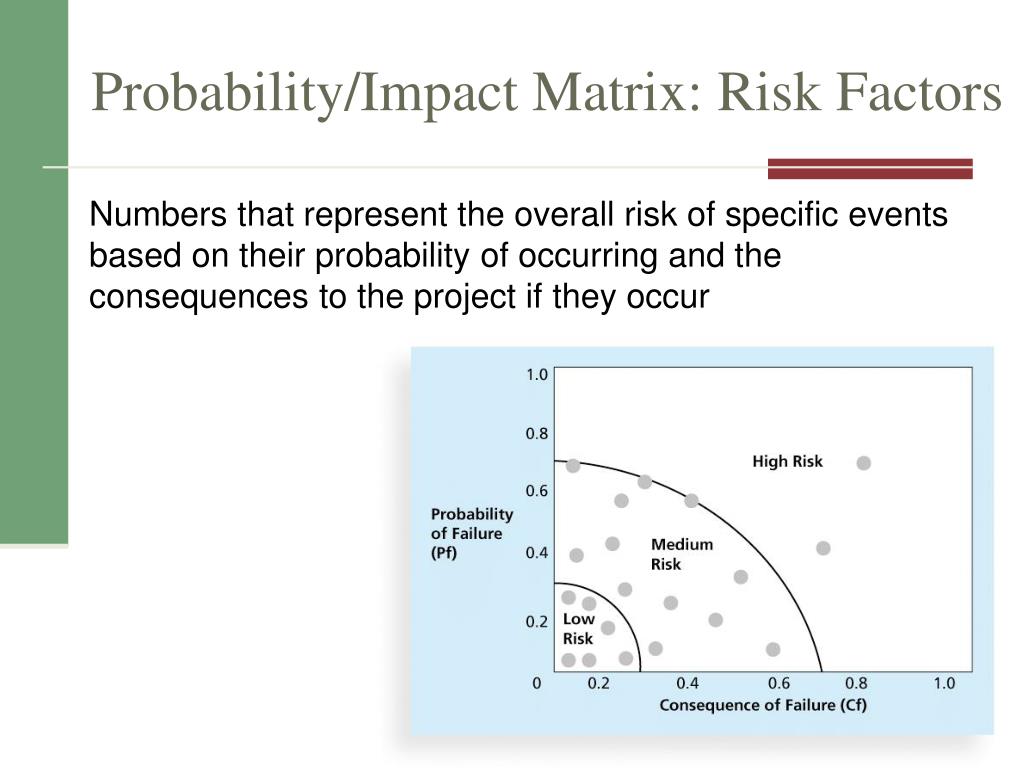
In non-PMP terms, this means you're guessing (or asking other experts to guess) at the probability a risk event will occur. Probability is expressed as a number from 0.0- which means there is no probability of the event occurring-to 1.0-which means there is 100% certainty the risk will occur.ĭetermining risk probability can be difficult because it's most commonly accomplished using expert judgment. The two responses added together equal 1.0. 50 chance you will not get heads on the flip. 50 chance that you'll get heads on the flip. In this coin-flipping example, you have a.
#Risk probability that an event will occur plus#
Note that the probability that an event will occur plus the probability that the event will not occur always equals 1.0. 50 probability of getting tails on the flip. Probability is the likelihood that an event will occur. When determining probabilities and impacts, you'll refer to the risk management plan element called "definitions of risk probability and impact." Probability Analyzing risks in this way allows you to determine which risks require the most aggressive management. This tool and technique assesses the probability that the risk events you've identified will occur, and it determines the effect their impacts have on the project objectives, including time, scope, quality, and cost.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
